Comprehending the Distinction Between PPOs and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
PPOs and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) are two of the most popular choices when it comes to the selection of health insurance plans.
Although both are managed care health plan types, they function differently and provide policyholders with unique advantages and restrictions. People can choose their healthcare coverage more wisely if they are aware of the main distinctions between these two types.
A Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): What is it?
Members of a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) must obtain the majority of their medical treatment from a network of physicians, hospitals, and other healthcare providers. By eliminating needless operations, enhancing patient care coordination, and placing a strong emphasis on preventive treatments, an HMO seeks to advance cost-effective care.
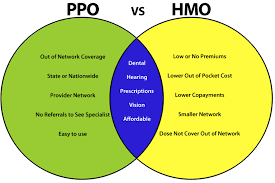
Primary Care Physician (PCP) Requirement: One of the most prominent aspects of an HMO is that they need members to select a PCP. This physician serves as the gatekeeper Maintenance for all other medical services. A member must first obtain a referral from their PCP in order to see a specialist or receive specialized treatment.
Network-Based Care: With the exception of emergencies, HMOs often mandate that members seek care exclusively from providers in their assigned network. Although the insurer may find it easier to control expenses as a result of this treatment restriction, the insured may have fewer options.
Reduced Out-of-Pocket Costs and Premiums: Compared to PPOs, HMOs usually have cheaper monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs. But in exchange, there is less freedom in
Maintenance Organizations
A PPO stands for Preferred Provider Organization.
Another kind of health insurance plan that gives members greater control over how they receive care is a PPO program. PPOs, as opposed to HMOs, do not require a recommendation in order for policyholders to see any physician or specialist, both inside and outside the network.
Important PPO Features:
There is no requirement for PPO members to choose a primary care physician. Without a reference, they are free to see any healthcare professional, both inside and outside the network. They now have more options when it comes to selecting healthcare providers.
Flexibility to See Out-of-Network Providers: PPOs give members the option to see out-of-network providers if they so choose Maintenance , even if they promote the use of in-network doctors by lowering out-of-pocket expenses.
Benefits and Drawbacks of PPOs vs HMOs
HMO benefits include:
Reduced Costs: For many people, HMOs are a more reasonable option because they often offer lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Coordinated Care: By emphasizing preventative care and requiring a PCP, HMOs contribute to the coordination of all patient care, which can improve health outcomes.
HMO drawbacks include:
Limited Choice: Being restricted to a particular network of providers and requiring referrals to see specialists are the main disadvantages of an HMO, which can be restrictive and inconvenient.
Lack of flexibility: It may be challenging or costly for a member to see an out-of-network physician or obtain specialty care without a referral.
PPO benefits include:
Flexibility: PPOs give members the ability to select physicians and specialists from both inside and outside the network without requiring referrals.
Convenience: PPOs give a major benefit to people who value convenience and the freedom to select their healthcare providers.
PPO drawbacks include:
Higher Costs: PPOs’ flexibility is accompanied with higher co-pays, deductibles, and premiums. This may make them more expensive, especially for people who don’t need to see experts frequently and are generally healthy.
Conclusion: Personal preferences, medical requirements, and financial constraints play a major role in deciding between an HMO and a PPO. An HMO might be a better choice if you’re searching for a less expensive solution and don’t mind having your primary care physician handle care coordination.
However, a PPO might be the best option if you want more flexibility and the freedom to see specialists or out-of-network physicians without requiring referrals.In the end, the option should be made after giving great thought to how much choice and flexibility you desire in your healthcare and how much you are ready to pay for that convenience.
