Telemedicine’s Growth and How It Affects Health Insurance
By giving patients virtual access to medical consultations, tests, and treatment plans, telemedicine has dramatically changed the healthcare scene in recent years. Driven by technological advancements, this novel approach to healthcare delivery has gained a lot of traction, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. As telemedicine continues to expand, it is also influencing the health insurance business, forcing changes in rules, reimbursement structures, and patient expectations
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is the practice of providing healthcare services remotely by using digital technologies, such as video calls, mobile apps, and remote monitoring devices. Although telemedicine has been around for decades, its growth has accelerated in recent years, largely because of the need for safer, more convenient healthcare options. Telemedicine encompasses a variety of remote healthcare options, such as teleconsultations, which are virtual appointments in which patients consult with doctors via chat, phone, or video.
Telemonitoring: The Telemedicine’s Growth and How It Affects Health Insurance use of devices to remotely monitor chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension; Teletherapy: Mental health services delivered through video or phone sessions; Telehealth Platforms: Comprehensive systems offering health advice, prescriptions, and referrals through digital interfaces.
Factors Driving the Rise of Telemedicine: The COVID-19 pandemic was a major catalyst that forced many healthcare systems to adopt telemedicine solutions as in-person visits became risky; Governments loosened regulations surrounding telehealth, expanding access and reimbursement policies, which accelerated its adoption.
Technological Advancements: The widespread use of high-speed internet, mobile devices, and cloud computing has made telemedicine more feasible and dependable; secure data exchange, high-definition video, and real-time communication tools have made virtual care more effective.
Demand from Consumers Telemedicine
provides quick access to care, particularly for routine consultations, follow-ups, and mental health services, all from the comfort of one’s own home. Cost-Effectiveness Because telemedicine eliminates the need for travel, lengthy wait times, and Telemedicine’s overhead costs associated with physical facilities, it is a more cost-effective option than in-person visits, which appeals to both patients and healthcare providers.
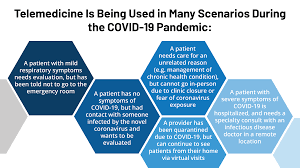
Impact of Telemedicine on Health Insurance As telemedicine has gained popularity, it has had a significant impact on the health insurance sector, which is evident in a number of important areas.
Expanding Coverage: Originally, health insurance Telemedicine’s plans did not cover telehealth services; however, insurers revised their policies in response to the increase in telemedicine use, and many health insurance companies now cover telemedicine services, such as virtual consultations and follow-up care. This trend is anticipated to continue even as pandemic-related restrictions loosen. Reimbursement Models.
One of the main obstacles to telemedicine was the lack of reimbursement from insurance companies, as they used to reimburse only in-person consultations.
Telemedicine’s
Efficiency and Cost Savings: Telemedicine offers health insurers the chance to cut expenses. Because virtual visits do not require real office space, staff, or other administrative expenses, they are frequently less expensive than in-person consultations.
Telemedicine can also aid in early diagnosis and preventative care, which may lessen the need for future hospital stays or more costly treatments.
Analytics and Data: Telemedicine platforms produce useful health data that may be examined to enhance patient outcomes and care. Insurers are using this information to forecast health trends, monitor patient compliance, and provide more Telemedicine’s individualized policies.
Better health outcomes and maybe fewer insurance claims can result from insurers using remote monitoring systems to keep an eye on chronic illnesses and make sure patients are adhering to recommended treatment programs Telemedicine’s
Customer Obstacles and Things to Think About
Notwithstanding the improvements, there are a number of difficulties with the growth of telemedicine:
Regulatory Issues: Different regulations pertaining to licensure, reimbursement, and data protection govern telemedicine differently Telemedicine’s in each country and region. To make sure they abide by regional regulations and offer the required coverage for telemedicine services, health insurers must negotiate these issues.
Technology Barriers: Although telemedicine may increase access to care, certain patients may still be unable to utilize remote services due to technological obstacles. For some communities, the usefulness of telemedicine may be limited by problems like inadequate technical infrastructure, low digital literacy, and lack of internet access.
Care Quality: Telemedicine may not be appropriate for many medical situations, despite its potential convenience. Certain medical conditions necessitate
The Prospects for Health Insurance and Telemedicine
The insurance sector and healthcare delivery are changing as a result of the emergence of telemedicine. Telemedicine is expected to become Telemedicine’s a permanent feature in the healthcare scene as the industry develops further, providing new ways to deliver care while enhancing in-person encounters.
In order to adapt to this change, health insurers will keep changing their regulations, offering telemedicine services more extensive coverage. Additionally, they will leverage analytics and data more and more to lower costs, improve health outcomes, and improve care management.
In the end, the emergence of telemedicine is a fascinating trend in the insurance and healthcare industries, benefiting both insurers and patients while increasing the accessibility, affordability, and effectiveness of healthcare for a larger population.
In conclusion
Telemedicine is transforming
