Comparing Public and Private Health Insurance in-depth
A vital part of contemporary healthcare systems, health insurance shields people from the financial burden of medical bills.
Both public and private health insurance systems, each with their own special traits, advantages, and difficulties, are offered in numerous nations.
In order to better comprehend the distinctions between public and private health insurance, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of each, this article will compare them.
Public health insurance: what is it
All citizens or residents should have access to public health insurance, which is a system run and financed by the government. The main goal is to guarantee that everyone, regardless of income level, has access to healthcare.
The government funds the program through taxes or national insurance contributions in the majority of nations with public healthcare systems Public and Private Health Insurance
The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom and Medicare (for the elderly and some disabled people) in the United States are two examples of public health insurance programs.
Important aspects of public health insurance include
Universal Coverage: Public health insurance frequently provides the general public with extensive coverage, guaranteeing that no one is turned away due to their financial situation or pre-existing medical issues.
Cost-Effectiveness: Public systems are frequently less expensive than private insurance since the government manages funding and administration.
Access to Basic Services: Hospital treatment, medical visits, and certain preventative services are among the necessary services that are usually covered by public insurance.
Private health insurance: what is it?
Private businesses provide private health insurance, which is often funded by premiums paid by employers or individuals. The coverage, rates, and provider networks of these plans can differ substantially.
Although private health insurance is optional in many nations, it is frequently viewed as an addition to public coverage in others, including the US.
Important aspects of private health insurance include:
Greater Flexibility and Choice: Private insurance plans usually give more services, such as access to a larger network of healthcare providers, private hospital rooms, and elective treatments.
Reduced Wait Times: A lot of private insurance plans provide quicker access to healthcare, including shorter wait times for specific surgeries or treatments.
Customization: People can select the coverage Public and Private Health Insurance that best meets their unique needs, such as dental, vision, or mental health care, under private health insurance.
Important Differences Between Private and Public Health Insurance
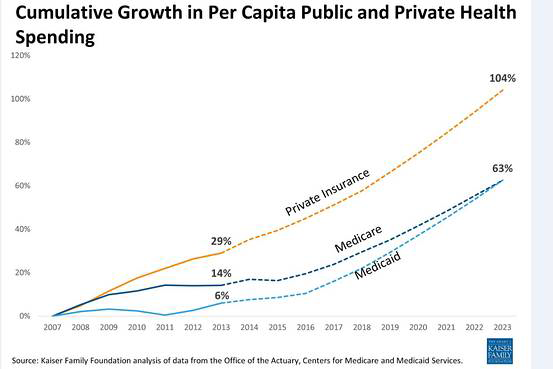
- The price of health insurance In public systems, taxes or contributions that are distributed to all citizens are usually used to pay for healthcare. Individual costs are typically lower because the system strives for affordability and inclusivity. For some services, certain nations may impose tiny out-of-pocket costs, co-pays, or premiums; however, they are typically negligible.
Private Health Insurance: Premiums for private health insurance vary according to age, health, and the scope of coverage, and they are typically more costly.
Common extra expenses include deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance. Particularly for comprehensive plans, private insurance premiums may exceed those of public insurance.
Public and Private Health Insurance
- Access to Healthcare Public Health Insurance: Although the standard and speed of service may differ, access to healthcare under public systems is typically assured. Public insurance usually covers a wide range of medical services in nations with universal health insurance, however there may be lengthy wait times for some treatments or elective surgery.
Faster access to healthcare services, such as elective procedures, consultations with specialists, and non-essential treatments, is made possible by private health insurance.
Wait times are usually shorter for private plans because they often have fewer patients to service. Nevertheless, coverage might be restricted to particular regions or healthcare providers.
- Care Quality
Public Health Insurance: In nations with public health systems, medical care can be of a high caliber, particularly during emergencies. But the resource
Private Health Insurance: Private Public and Private Health Insurance insurance typically provides more comfort, such as access to world-class physicians, private hospital rooms, and speedier service.
Better clinical results, however, might not necessarily result from this because expensive private providers do not always have the same caliber of medical personnel or equipment as the top public hospitals.
- Inclusion and Equity
Insurance for Public Health: Emphasizing equity and offering universal coverage to all citizens, irrespective of their age, income, or health status, is a defining characteristic of public health insurance. It guarantees access to healthcare services even for those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds.
Private Health Insurance: People in higher income levels who can afford the premiums, however, frequently have easier access to private insurance. ThoseFlexibility and Choice
Public Health Insurance: In general, public insurance plans provide fewer options for medical professionals.
Patients frequently have to use medical professionals that are affiliated with the public system, which can restrict their options.
Private health insurance: Plans offered by private companies give people more options, enabling them to choose from a wider variety of physicians, hospitals, and specialists.
One of the main benefits of private insurance is its flexibility, which makes it a desirable choice for people who appreciate individualized treatment.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Private and Public Health Insurance
Public health insurance benefits include:
Affordability: Usually less expensive for people because of tax funding.
Regardless of socioeconomic situation, universal access guarantees that all citizens have access to healthcare.
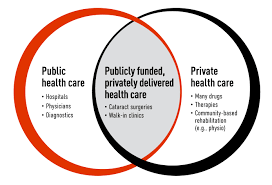
All-inclusive Coverage: Provides coverage for a variety of healthcare services.
The drawbacks of public health insurance Public and Private Health Insurance
Long Wait Times Public and Private Health Insurance
Because of increased demand, non-urgent services may have lengthier wait times.
Possibility of Overburdened services: Underfunding or a lack of personnel may cause public services to become overburdened, which would lower their quality.
Private health insurance benefits include:
Quicker Care Access: faster access to elective therapies and shorter wait times.
Choice of Providers: More freedom to select medical specialists and facilities.
Access to extra services, such private rooms or specialty treatments, is known as enhanced services.
The drawbacks of private health insurance
Expensive: Out-of-pocket expenses and premiums can be high, especially for comprehensive plans.
Exclusionary: People with pre-existing conditions or those with lesser incomes might not be able to receive it.
In conclusion
Each system has unique benefits and drawbacks, making the argument between private and public health insurance complicated. Although public health insurance is generally more equal and offers everyone access to necessary care, frequently at a reduced cost, it may encounter difficulties such as resource constraints and higher wait times.
Despite providing greater Public and Private Health Insurance options and speedier access to care, private health insurance is frequently more expensive and may result in unequal access to healthcare.
In the end, a nation’s economic circumstances, healthcare system, and social beliefs all influence the best system. Some nations combine the two, offering private options to those who can pay them while maintaining public health care for basic services.
Choosing between private and public health insurance frequently comes down to personal preferences.
Public and Private Health Insurance